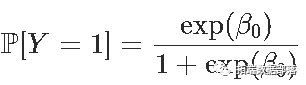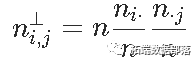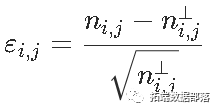全文下载链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=18266
本文通过R语言建立广义线性模型(GLM)、多项式回归和广义可加模型(GAM)来预测谁在1912年的泰坦尼克号沉没中幸存下来。
拓端该视频号动态不可引用str(titanic)
数据变量为:
Survived:乘客存活指标(如果存活则为1)Pclass:旅客舱位等级Sex:乘客性别Age:乘客年龄SibSp:兄弟姐妹/配偶人数Parch:父母/子女人数Embarked:登船港口Name:旅客姓名
最后一个变量使用不多,因此我们将其删除,
titanic = titanic[,1:7]
现在,我们回答问题:
幸存的旅客比例是多少?
简单的答案是
mean(titanic$Survived)[1] 0.3838384
可以在下面的列联表中找到
table(titanic$Survived)/nrow(titanic)0 10.6161616 0.3838384
或此处幸存者的38.38 %。也就是说,也可以通过不对任何解释变量进行逻辑回归来获得(换句话说,仅对常数进行回归)。回归给出了:
Coefficients:(Intercept)-0.4733 Degrees of Freedom: 890 Total (i.e. Null); 890 ResidualNull Deviance: 1187Residual Deviance: 1187 AIC: 1189
给出β0的值,并且由于生存概率为
我们通过考虑
exp(-0.4733)/(1+exp(-0.4733))[1] 0.3838355
我们也可以使用predict函数
predict(glm(Survived~1, family=binomial,type="response")[1]10.3838384
此外,在概率回归中也适用,
reg=glm(Survived~1, family=binomial(link="probit"),data=titanic)predict(reg,type="response")[1]10.3838384
幸存的头等舱乘客的比例是多少?
我们只看头等舱的人,
[1] 0.6296296
约63%存活。我们可以进行逻辑回归
Coefficients:(Intercept) Pclass2 Pclass30.5306 -0.6394 -1.6704 Degrees of Freedom: 890 Total (i.e. Null); 888 ResidualNull Deviance: 1187Residual Deviance: 1083 AIC: 1089
由于第1类是参考类,因此我们照旧考虑
exp(0.5306)/(1+exp(0.5306))[1] 0.629623
predict预测
predict(reg,newdata=data.frame(Pclass="1"),type="response")10.6296296
我们可以尝试概率回归,我们得到的结果是一样的,
predict(reg,newdata=data.frame(Pclass="1"),type="response")10.6296296
卡方独立性测试 :在生存与否之间的检验统计量是多少?
卡方检验的命令如下
chisq.test(table( Survived, Pclass)) Pearson's Chi-squared test data: table( Survived, Pclass)X-squared = 102.89, df = 2, p-value < 2.2e-16
我们有一个列联表,如果变量是独立的,我们有 ,然后是统计量 ,我们可以看到,对测试的贡献
1.
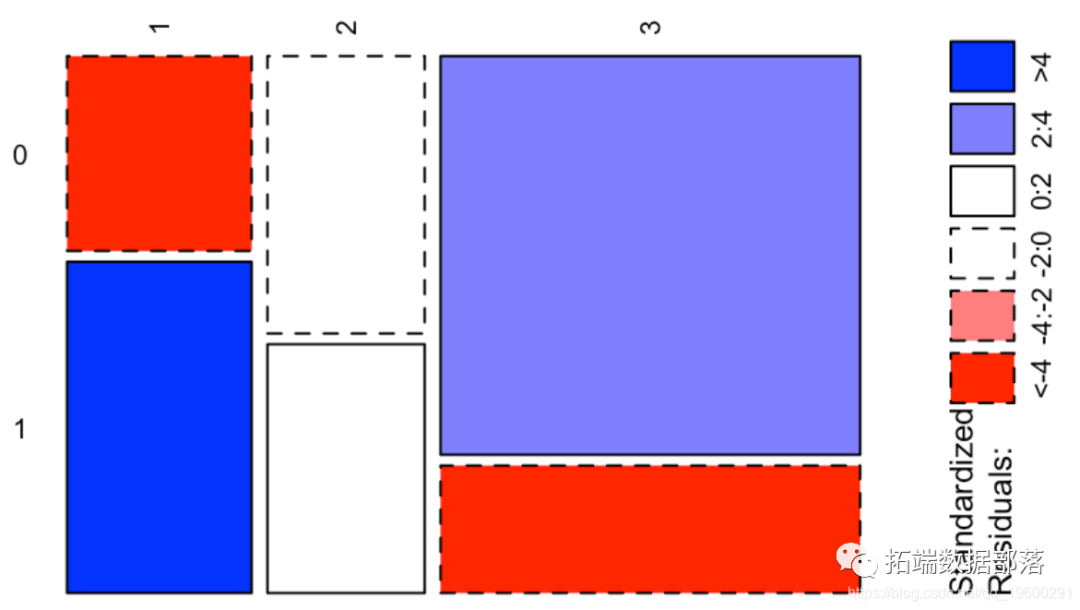
1 2 30 -4.601993 -1.537771 3.9937031 5.830678 1.948340 -5.059981
这给了我们很多信息:我们观察到两个正值,分别对应于“幸存”和“头等舱”与“无法幸存”和“三等舱”之间的强(正)关联,以及两个很强的负值,对应于“生存”和“第三等”之间的强烈负相关,以及“无法幸存”和“头等舱”。我们可以在下图上可视化这些值
ass(table( Survived, Pclass), shade = TRUE, las=3)
然后我们必须进行逻辑回归,并预测两名模拟乘客的生存概率
点击标题查阅往期内容
R语言贝叶斯广义线性混合(多层次/水平/嵌套)模型GLMM、逻辑回归分析教育留级影响因素数据
01
02
03
04
假设我们有两名乘客
newbase = data.frame(Pclass = as.factor(c(1,3)),Sex = as.factor(c("female","male")),Age = c(17,20),SibSp = c(1,0),Parch = c(2,0),
让我们对所有变量进行简单回归,
Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)(Intercept) 16.830381 607.655774 0.028 0.97790Pclass2 -1.268362 0.298428 -4.250 2.14e-05 ***Pclass3 -2.493756 0.296219 -8.419 < 2e-16 ***Sexmale -2.641145 0.222801 -11.854 < 2e-16 ***Age -0.043725 0.008294 -5.272 1.35e-07 ***SibSp -0.355755 0.128529 -2.768 0.00564 **Parch -0.044628 0.120705 -0.370 0.71159EmbarkedC -12.260112 607.655693 -0.020 0.98390EmbarkedQ -13.104581 607.655894 -0.022 0.98279EmbarkedS -12.687791 607.655674 -0.021 0.98334---Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1) Null deviance: 964.52 on 713 degrees of freedomResidual deviance: 632.67 on 704 degrees of freedom(177 observations deleted due to missingness)AIC: 652.67 Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 13
两个变量并不重要。我们删除它们
Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)(Intercept) 4.334201 0.450700 9.617 < 2e-16 ***Pclass2 -1.414360 0.284727 -4.967 6.78e-07 ***Pclass3 -2.652618 0.285832 -9.280 < 2e-16 ***Sexmale -2.627679 0.214771 -12.235 < 2e-16 ***Age -0.044760 0.008225 -5.442 5.27e-08 ***SibSp -0.380190 0.121516 -3.129 0.00176 **---Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1) Null deviance: 964.52 on 713 degrees of freedomResidual deviance: 636.56 on 708 degrees of freedom(177 observations deleted due to missingness)AIC: 648.56 Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
我们有年龄这样的连续变量时,我们可以进行多项式回归
Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)(Intercept) 3.0213 0.2903 10.408 < 2e-16 ***Pclass2 -1.3603 0.2842 -4.786 1.70e-06 ***Pclass3 -2.5569 0.2853 -8.962 < 2e-16 ***Sexmale -2.6582 0.2176 -12.216 < 2e-16 ***poly(Age, 3)1 -17.7668 3.2583 -5.453 4.96e-08 ***poly(Age, 3)2 6.0044 3.0021 2.000 0.045491 *poly(Age, 3)3 -5.9181 3.0992 -1.910 0.056188 .SibSp -0.5041 0.1317 -3.828 0.000129 ***---Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1) Null deviance: 964.52 on 713 degrees of freedomResidual deviance: 627.55 on 706 degrees of freedomAIC: 643.55 Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
但是解释参数变得很复杂。我们注意到三阶项在这里很重要,因此我们将手动进行回归
Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)(Intercept) 5.616e+00 6.565e-01 8.554 < 2e-16 ***Pclass2 -1.360e+00 2.842e-01 -4.786 1.7e-06 ***Pclass3 -2.557e+00 2.853e-01 -8.962 < 2e-16 ***Sexmale -2.658e+00 2.176e-01 -12.216 < 2e-16 ***Age -1.905e-01 5.528e-02 -3.446 0.000569 ***I(Age^2) 4.290e-03 1.854e-03 2.314 0.020669 *I(Age^3) -3.520e-05 1.843e-05 -1.910 0.056188 .SibSp -5.041e-01 1.317e-01 -3.828 0.000129 ***---Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1) Null deviance: 964.52 on 713 degrees of freedomResidual deviance: 627.55 on 706 degrees of freedomAIC: 643.55 Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 5
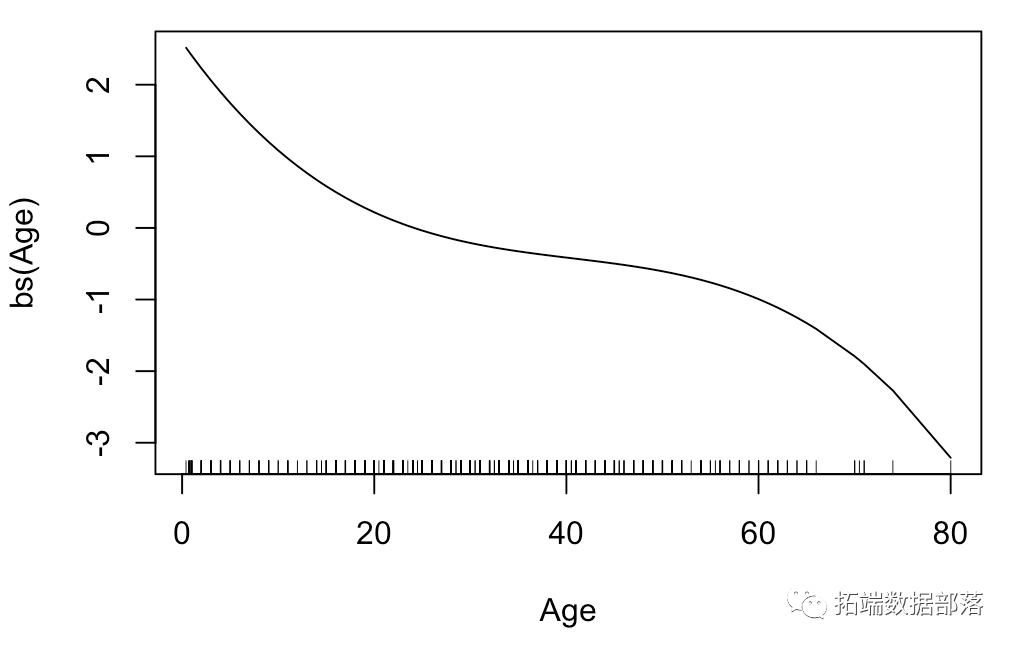
可以看到,p值是相同的。简而言之,将年龄转换为年龄的非线性函数是有意义的。可以可视化此函数
plot(xage,yage,xlab="Age",ylab="",type="l")
实际上,我们可以使用样条曲线。广义可加模型( gam )是完美的可视化工具
(Dispersion Parameter for binomial family taken to be 1) Null Deviance: 964.516 on 713 degrees of freedomResidual Deviance: 627.5525 on 706 degrees of freedomAIC: 643.5525177 observations deleted due to missingness Number of Local Scoring Iterations: 4 Anova for Parametric EffectsDf Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)Pclass 2 26.72 13.361 11.3500 1.407e-05 ***Sex 1 131.57 131.573 111.7678 < 2.2e-16 ***bs(Age) 3 22.76 7.588 6.4455 0.0002620 ***SibSp 1 14.66 14.659 12.4525 0.0004445 ***Residuals 706 831.10 1.177---Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
我们可以看到年龄变量的变换,
并且我们发现变换接近于我们的3阶多项式。我们可以添加置信带,从而可以验证该函数不是真正的线性
我们现在有三个模型。最后给出了两个模拟乘客的预测,
predict(reg,newdata=newbase,type="response")1 20.9605736 0.1368988predict(reg3,newdata=newbase,type="response")1 20.9497834 0.1218426predict(regam,newdata=newbase,type="response")1 20.9497834 0.1218426
可以看到莱昂纳多·迪卡普里奥( Leonardo DiCaprio) 有大约12%的幸存机会(考虑到他的年龄,他有三等票,而且船上没有家人)。