最近我被要求撰写关于金融时间序列的copulas的调查。从读取数据中获得各种模型的描述,包括一些图形和统计输出。
> oil = read.xlsx(temp,sheetName =“DATA”,dec =“,”)
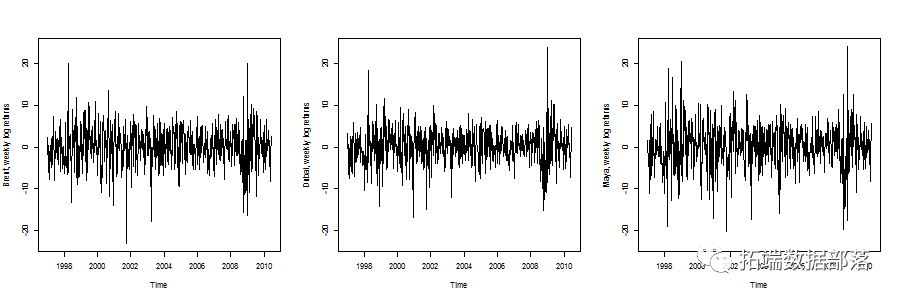
然后我们可以绘制这三个时间序列
1 1997-01-10 2.73672 2.25465 3.3673 1.5400 2 1997-01-17 -3.40326 -6.01433 -3.8249 -4.1076 3 1997-01-24 -4.09531 -1.43076 -6.6375 -4.6166 4 1997-01-31 -0.65789 0.34873 0.7326 -1.5122 5 1997-02-07 -3.14293 -1.97765 -0.7326 -1.8798 6 1997-02-14 -5.60321 -7.84534 -7.6372 -11.0549
这个想法是在这里使用一些多变量ARMA-GARCH过程。这里的启发式是第一部分用于模拟时间序列平均值的动态,第二部分用于模拟时间序列方差的动态。
本文考虑了两种模型
- 关于ARMA模型残差的多变量GARCH过程(或方差矩阵动力学模型)
- 关于ARMA-GARCH过程残差的多变量模型(基于copula)
因此,这里将考虑不同的序列,作为不同模型的残差获得。我们还可以将这些残差标准化。
ARMA模型
> fit1 = arima(x = dat [,1],order = c(2,0,1)) > fit2 = arima(x = dat [,2],order = c(1,0,1)) > fit3 = arima(x = dat [,3],order = c(1,0,1)) > m < - apply(dat_arma,2,mean) > v < - apply(dat_arma,2,var) > dat_arma_std < - t((t(dat_arma)-m)/ sqrt(v))
ARMA-GARCH模型
> fit1 = garchFit(formula = ~arma(2,1)+ garch(1,1),data = dat [,1],cond.dist =“std”) > fit2 = garchFit(formula = ~arma(1,1)+ garch(1,1),data = dat [,2],cond.dist =“std”) > fit3 = garchFit(formula = ~arma(1,1)+ garch(1,1),data = dat [,3],cond.dist =“std”) > m_res < - apply(dat_res,2,mean) > v_res < - apply(dat_res,2,var) > dat_res_std = cbind((dat_res [,1] -m_res [1])/ sqrt(v_res [1]),(dat_res [,2] -m_res [2])/ sqrt(v_res [2]),(dat_res [ ,3] -m_res [3])/ SQRT(v_res [3]))
多变量GARCH模型
可以考虑的第一个模型是协方差矩阵的多变量EWMA,
> ewma = EWMAvol(dat_res_std,lambda = 0.96)
波动性
> emwa_series_vol = function(i = 1){ + lines(Time,dat_arma [,i] + 40,col =“gray”) + j = 1 + if(i == 2)j = 5 + if(i == 3)j = 9
隐含相关性
> emwa_series_cor = function(i = 1,j = 2){ + if((min(i,j)== 1)&(max(i,j)== 2)){ + a = 1; B = 9; AB = 3} + r = ewma $ Sigma.t [,ab] / sqrt(ewma $ Sigma.t [,a] * + ewma $ Sigma.t [,b]) + plot(Time,r,type =“l”,ylim = c(0,1)) +}
多变量GARCH,即BEKK(1,1)模型,例如使用:
> bekk = BEKK11(dat_arma) > bekk_series_vol function(i = 1){ + plot(Time, $ Sigma.t [,1],type =“l”, + ylab = (dat)[i],col =“white”,ylim = c(0,80)) + lines(Time,dat_arma [,i] + 40,col =“gray”) + j = 1 + if(i == 2)j = 5 + if(i == 3)j = 9 > bekk_series_cor = function(i = 1,j = 2){ + a = 1; B = 5; AB = 2} + a = 1; B = 9; AB = 3} + a = 5; B = 9; AB = 6} + r = bk $ Sigma.t [,ab] / sqrt(bk $ Sigma.t [,a] * + bk $ Sigma.t [,b])
从单变量GARCH模型中模拟残差
第一步可能是考虑残差的一些静态(联合)分布。单变量边缘分布是
边缘密度的轮廓(使用双变量核估计获得)
也可以将copula密度可视化(上面有一些非参数估计,下面是参数copula)
> copula_NP = function(i = 1,j = 2){ + n = nrow(uv) + s = 0.3 + norm.cop < - normalCopula(0.5) + norm.cop < - normalCopula(fitCopula(norm.cop,uv)@estimate) + dc = function(x,y)dCopula(cbind(x,y),norm.cop) + ylab = names(dat)[j],zlab =“copule Gaussienne”,ticktype =“detailed”,zlim = zl) + + t.cop < - tCopula(0.5,df = 3) + t.cop < - tCopula(t.fit [1],df = t.fit [2]) + ylab = names(dat)[j],zlab =“copule de Student”,ticktype =“detailed”,zlim = zl) +}
可以考虑这个 函数,
计算三个序列的的经验版本,并将其与一些参数版本进行比较,
> > lambda = function(C){ + l = function(u)pcopula(C,cbind(u,u))/ u + v = Vectorize(l)(u) + return(c(v,rev(v))) +} > > graph_lambda = function(i,j){ + X = dat_res + U = rank(X [,i])/(nrow(X)+1) + V = rank(X [,j])/(nrow(X)+1) + normal.cop < - normalCopula(.5,dim = 2) + t.cop < - tCopula(.5,dim = 2,df = 3) + fit1 = fitCopula(normal.cop,cbind(U,V),method =“ml”) d(U,V),method =“ml”) + C1 = normalCopula(fit1 @ copula @ parameters,dim = 2) + C2 = tCopula(fit2 @ copula @ parameters [1],dim = 2,df = trunc(fit2 @ copula @ parameters [2])) +
但人们可能想知道相关性是否随时间稳定。
> time_varying_correl_2 = function(i = 1,j = 2, + nom_arg =“Pearson”){ + uv = dat_arma [,c(i,j)] nom_arg))[1,2] +} > time_varying_correl_2(1,2) > time_varying_correl_2(1,2,“spearman”) > time_varying_correl_2(1,2,“kendall”)
斯皮尔曼与时变排名相关系数
或肯德尔 相关系数
为了模型的相关性,考虑DCC模型(S)
> m2 = dccFit(dat_res_std) > m3 = dccFit(dat_res_std,type =“Engle”) > R2 = m2 $ rho.t > R3 = m3 $ rho.t
要获得一些预测, 使用例如
> garch11.spec = ugarchspec(mean.model = list(armaOrder = c(2,1)),variance.model = list(garchOrder = c(1,1),model =“GARCH”)) > dcc.garch11.spec = dccspec(uspec = multispec(replicate(3,garch11.spec)),dccOrder = c(1,1), distribution =“mvnorm”) > dcc.fit = dccfit(dcc.garch11.spec,data = dat) > fcst = dccforecast(dcc.fit,n.ahead = 200)